Gorynychus
- Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text into the English Wikipedia.
- Consider adding a topic to this template: there are already 1,490 articles in the main category, and specifying
|topic=will aid in categorization. - Do not translate text that appears unreliable or low-quality. If possible, verify the text with references provided in the foreign-language article.
- You must provide copyright attribution in the edit summary accompanying your translation by providing an interlanguage link to the source of your translation. A model attribution edit summary is
Content in this edit is translated from the existing French Wikipedia article at [[:fr:Gorynychus]]; see its history for attribution. - You may also add the template
{{Translated|fr|Gorynychus}}to the talk page. - For more guidance, see Wikipedia:Translation.
| Gorynychus Temporal range: Mid Permian PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Holotype skull of G. masyutinae | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Synapsida |
| Clade: | Therapsida |
| Clade: | †Therocephalia |
| Genus: | †Gorynychus Kammerer & Masyutin, 2018 |
| Type species | |
| †Gorynychus masyutinae Kammerer & Masyutin, 2018 | |
| Other species | |
| |
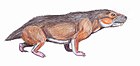
Gorynychus is a genus of therocephalian from the mid-Permian from Kotelnich, Russia. The genus contains two species, G. masyutinae and G. sundyrensis. It was named after the three-headed dragon Zmey Gorynych (Змей Горыныч) from Russian mythology.[1][2][3]
Description

G. masyutinae, only known from its holotype, was wolf-sized and appears to have represented the largest predator in the Kotelnich fauna. Like many theriodonts, it had strongly developed and prominent canine teeth.[1]
Paleoecology
The discovery of such a large therocephalian as the apex predator of its environment coupled with the discovery of a smaller gorgonopsid, the smaller and nocturnal Nochnitsa, in the same formation indicates that a faunal turnover was occurring at the time, with gorgonopsians taking over the therocephalians' role as the dominant predators in their environment.[2]
References
- ^ a b Kammerer, CF; Masyutin, V. (2018). "A new therocephalian (Gorynychus masyutinae gen. et sp. nov.) from the Permian Kotelnich locality, Kirov Region, Russia". PeerJ. 6: e4933. doi:10.7717/peerj.4933. PMC 5995100. PMID 29900076.
- ^ a b North Carolina Museum of Natural Sciences (June 8, 2018). "'Monstrous' new Russian saber-tooth fossils clarify early evolution of mammal lineage". ScienceDaily. Retrieved June 13, 2018.
- ^ Suchkova, J.A.; Golubev, V.K. (2019). "New Permian therocephalian (Therocephalia, Theromorpha) from the Sundyr Assemblage of Eastern Europe". Paleontological Journal (4): 87–92. doi:10.1134/S0031031X19040123.
- v
- t
- e
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||
| 
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
 Category
Category
 | This therapsid-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e